File:SPM overview.jpg
SPM_overview.jpg (703 × 440 pixels, file size: 74 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Captions
Captions

|
This image could be re-created using vector graphics as an SVG file. This has several advantages; see Commons:Media for cleanup for more information. If an SVG form of this image is available, please upload it and afterwards replace this template with
{{vector version available|new image name}}.
It is recommended to name the SVG file “SPM overview.svg”—then the template Vector version available (or Vva) does not need the new image name parameter. |
This image was uploaded in the JPEG format even though it consists of non-photographic data. This information could be stored more efficiently or accurately in the PNG or SVG format. If possible, please upload a PNG or SVG version of this image without compression artifacts, derived from a non-JPEG source (or with existing artifacts removed). After doing so, please tag the JPEG version with {{Superseded|NewImage.ext}} and remove this tag. This tag should not be applied to photographs or scans. If this image is a diagram or other image suitable for vectorisation, please tag this image with {{Convert to SVG}} instead of {{BadJPEG}}. If not suitable for vectorisation, use {{Convert to PNG}}. For more information, see {{BadJPEG}}. |
Summary
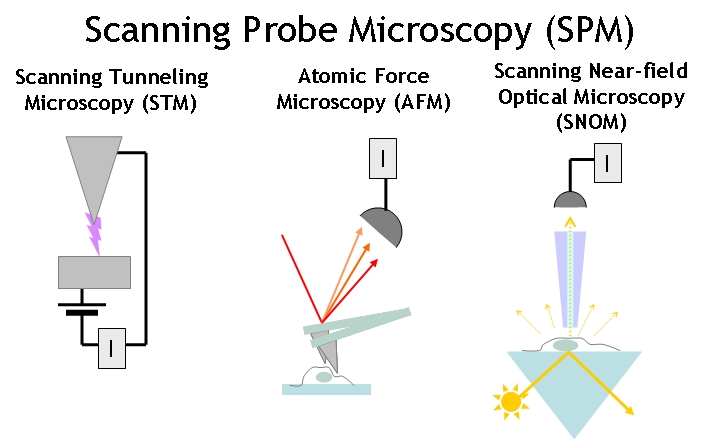
editOverview of the main types of Scannig Probe Microscope types:
Scanning tunneling microscope (STM) - using the tunneling current I between the outermost atom of a conducting probe within an atomic distance from a substrate to map out the sample topography and electrical properties.
Atomic force microscope (AFM) - using the van der Waals forces or contact forces between a tip and the sample to measure the sample topography or mechanical properties.
Scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) - using the scattered light through a sub-wavelenght aperture to form an image.
- Illustration by Kristian Molhave
- Please acknowledge the Opensource Handbook of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology if you use illustrations from it.
Licensing
edit- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:39, 17 November 2006 |  | 703 × 440 (74 KB) | KristianMolhave (talk | contribs) | Overview of the main types of Scannig Probe Microscope types: *scanning tunneling microscope (STM) *Atomic force microscope (AFM) *Scanning Near-field Optical Microscope (SNOM) *Illustration by [http://kristian.molhave.dk Kristian Molhave] *Please acknow |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following page uses this file:
File usage on other wikis
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on en.wikibooks.org
- Usage on nl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on pl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ru.wikipedia.org
- Usage on uk.wikipedia.org
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| _error | 0 |
|---|