阿坎酸
阿坎酸(英語:)以Campral及Alglutol(戒酒妥)等品牌銷售,是一種與治療酒精使用疾患(酗酒)諮詢合併使用的藥物。[1][2]
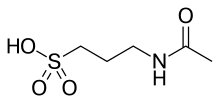 | |
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 读音 | /əˈkæmproʊseɪt/ |
| 商品名 | Campral、Alglutol,及其他 |
| 其他名稱 | N-乙酰基高牛磺酸(N-Acetyl homotaurine), 阿坎酸鈣 (JAN JP), 阿坎酸鈣 (USAN US) |
| 懷孕分級 |
|
| 给药途径 | 口服給藥[1] |
| ATC碼 | |
| 法律規範狀態 | |
| 法律規範 |
|
| 藥物動力學數據 | |
| 生物利用度 | 11%[1] |
| 血漿蛋白結合率 | 可忽略不計[1] |
| 药物代谢 | 無[1] |
| 生物半衰期 | 20 - 33小時[1] |
| 排泄途徑 | 腎臟[1] |
| 识别 | |
| |
| CAS号 | 77337-76-9 |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.071.495 |
| 化学 | |
| 化学式 | C5H11NO4S |
| 摩尔质量 | 181.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D模型(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
阿坎酸被認為可穩定大腦的神經傳遞,這些訊號傳遞會因酒精戒斷而受干擾。[3]對大多數患者而言,單獨使用阿坎酸並非有效的治療方法。[4]研究發現將阿坎酸與社會心理支持結合時效果會最佳,因為該藥物有助於減少飲酒數量,也有達到完全戒酒的效果。[2][5][6]
服用此藥物的嚴重副作用有過敏反應、心律不整以及低血壓或是高血壓,而較不嚴重的副作用有頭痛、失眠和勃起功能障礙。[7]最常見的副作用是腹瀉。[8]目前尚不清楚個體於懷孕期間使用是否對胎兒有安全的問題。[9][10]
此藥物被列入世界衛生組織基本藥物標準清單之中。[11]
醫療用途
有酒精使用障礙的患者在接受諮詢,並同時服用阿坎酸時會非常有用。[2]在三到十二個月的治療期間,完全不喝酒的人數和患者不喝酒的天數會增加。[2]它在維持戒酒方面似乎與納曲酮一樣有效,[12]然而納曲酮在減少酒精渴望和酗酒方面效果稍好,[13]同時在歐洲以外,而治療服務不太健全的地區,使用阿坎酸的效果往往會較差。[14]
用藥禁忌
阿坎酸主要經由腎臟排除。對於腎功能中度受損的患者(肌酸酐清除率在30毫升/分鐘和50毫升/分鐘之間),建議將使用劑量降低。[1][15]對藥物中阿坎酸鈣或其任何成分有強烈過敏反應的人也應禁止使用。[15]
不良影響
此藥物在美國銷售的標籤上會列有服用會與自殺行為、重性憂鬱疾患和腎衰竭增加有關聯的警告。[1]
在臨床試驗中,對停止服用者導致的不良反應有腹瀉、噁心、憂鬱和焦慮。[1]
潛在的副作用包括頭痛、腹痛、背痛、肌肉痛、關節痛、胸痛、感染、類流感症狀、發冷、心悸、高血壓、昏厥、嘔吐、胃部不適、便秘、食慾增加、體重增加、水腫、嗜睡、性慾減退、勃起功能障礙、健忘、思考障礙、視力異常、味覺異常、顫抖、流鼻涕、咳嗽、呼吸困難、喉嚨痛、支氣管炎和皮疹。[1]
藥理學

藥效學
阿坎酸的藥效學很複雜且尚未被完全了解,[16][17][18]然而它被認為可作為NMDA受體拮抗劑和[[GABAA受體]]的正變構調節劑。[17][18]
此藥物與大多數其他藥物不同,其對這些受體產生的活性是間接性的。[19]抑制GABAB系統被認為會間接導致GABAA受體增強。[19]對NMDA受體的影響具有劑量依賴性,藥物似乎在低濃度下可增強受體活性,而在較高濃度時會有抑制作用,可抵消患者在發生酒精戒斷情況下NMDA受體過度激活狀態。[20]
乙醇和苯二氮平類藥物透過與GABAA受體結合,將具有抑制神經傳導作用的GABA功能增強,而對中樞神經系統發揮作用(即此藥物充當這些受體的正變構調節劑)。[17][4]對有酒精使用疾患的患者,發生耐受性的主要機制之一是GABAA受體下調(即這些受體對GABA變得不太敏感)。[4]而當個體停止飲酒後,正常的GABA生產就會導致戒斷症狀出現,[4]而導致神經元過度興奮。阿坎酸的作用機制之一是透過正變構受體調節,增強GABAA受體的GABA訊號傳導。[17][18]據稱此藥物能以一種新穎的方式打開氯離子通道,而不需要GABA作為輔助因子,因此比苯二氮平類藥物更不易產生依賴性。阿坎酸已成功用於控制因鼓膜張肌痙攣而導致的耳鳴、聽覺過敏、耳痛和飲酒期間的內耳壓力。[21]
此外,酒精也會抑制NMDA受體的活性。[22][23]長期飲酒會導致這些受體過度生產(上調)。突然戒酒後會導致這些大量生產的NMDA受體比正常情況更為活躍,而產生震顫性譫妄和興奮性毒性而導致神經元死亡的情況。[24]戒酒會導致麩胺酸等興奮性神經傳導物質釋放激增,而過度激活NMDA受體。[25]阿坎酸可減少麩氨酸的激增。[26]該藥物還表現出可保護實驗室培養大鼠細胞免受乙醇戒斷引起的興奮性毒性,[27]以及受乙醇戒斷加上麩氨酸暴露的影響。[28]
歷史
阿坎酸由默克集團子公司Lipha所開發。[30]於1989年獲准在歐洲用於治療酒精依賴。[31]
藥業公司Forest Laboratories於2001年10月取得藥物在美國的銷售權。[30][32]
該藥物於2004年7月獲得美國食品藥物管理局(FDA)核准用於醫療用途。[33]
截至2015年,名為Confluence Pharmaceuticals的藥業公司在開發阿坎酸作為X染色體易裂症的治療法。此藥物在2013年被FDA授予孤兒藥地位,並於2014年也被歐洲藥品管理局(EMA)授予孤兒藥地位。[35]
社會與文化
"阿坎酸"是此藥物的國際非專有藥名(INN)和英國核准藥名(BAN)。 "阿坎酸鈣"是美國通用名(USAN)和日本接受名(JAN)。它在技術上也稱為N-乙酰基高牛磺酸(N-acetylhomotaurine )或乙醯高牛磺酸(acetylhomotaurinate)。
此藥物以Campral[1]及Alglutol等品牌銷售。
參見
- (PDF). FDA. January 2012 [2017-11-27]. For label updates see FDA index page for NDA 021431
- Plosker GL. . Drugs. July 2015, 75 (11): 1255–1268. PMID 26084940. S2CID 19119078. doi:10.1007/s40265-015-0423-9.
- Williams SH. . American Family Physician. November 2005, 72 (9): 1775–1780 [2006-11-29]. PMID 16300039. (原始内容存档于2007-09-29).
- Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE, Holtzman DM. . 3rd. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2015. ISBN 9780071827706.
It has been hypothesized that long-term ethanol exposure alters the expression or activity of specific GABAA receptor subunits in discrete brain regions. Regardless of the underlying mechanism, ethanol-induced decreases in GABAA receptor sensitivity are believed to contribute to ethanol tolerance, and also may mediate some aspects of physical dependence on ethanol. ... Detoxification from ethanol typically involves the administration of benzodiazepines such as chlordiazepoxide, which exhibit cross-dependence with ethanol at GABAA receptors (Chapters 5 and 15). A dose that will prevent the physical symptoms associated with withdrawal from ethanol, including tachycardia, hypertension, tremor, agitation, and seizures, is given and is slowly tapered. Benzodiazepines are used because they are less reinforcing than ethanol among alcoholics. Moreover, the tapered use of a benzodiazepine with a long half-life makes the emergence of withdrawal symptoms less likely than direct withdrawal from ethanol. ... Unfortunately, acamprosate is not adequately effective for most alcoholics.
- Mason BJ. . The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2001, 62 (Suppl 20): 42–48. PMID 11584875.
- Nutt DJ, Rehm J. . Journal of Psychopharmacology. January 2014, 28 (1): 3–7. PMID 24399337. S2CID 36860967. doi:10.1177/0269881113512038.
- . drugs.com. 2005-03-25 [2007-01-08]. (原始内容存档于2006-12-22).
- Wilde MI, Wagstaff AJ. . Drugs. June 1997, 53 (6): 1038–1053. PMID 9179530. S2CID 195691152. doi:10.2165/00003495-199753060-00008.
- . Drugs.com (英语).
- Haber P, Lintzeris N, Proude E, Lopatko O. (PDF). Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. [2023-02-20].
- World Health Organization. . Geneva: World Health Organization. 2023. hdl:10665/371090
 . WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02. - Kranzler HR, Soyka M. . JAMA. August 2018, 320 (8): 815–824. PMC 7391072
 . PMID 30167705. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.11406.
. PMID 30167705. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.11406. - Maisel NC, Blodgett JC, Wilbourne PL, Humphreys K, Finney JW. . Addiction. February 2013, 108 (2): 275–293. PMC 3970823
 . PMID 23075288. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.04054.x.
. PMID 23075288. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.04054.x. - Donoghue K, Elzerbi C, Saunders R, Whittington C, Pilling S, Drummond C. . Addiction. June 2015, 110 (6): 920–930. PMID 25664494. doi:10.1111/add.12875.
- Saivin S, Hulot T, Chabac S, Potgieter A, Durbin P, Houin G. . Clinical Pharmacokinetics. November 1998, 35 (5): 331–345. PMID 9839087. S2CID 34047050. doi:10.2165/00003088-199835050-00001.
- . IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [2017-11-26].
Due to the complex nature of this drug's MMOA, and a paucity of well defined target affinity data, we do not map to a primary drug target in this instance.
- . IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [2017-11-26].
Acamprosate is a NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist and a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors.
Marketed formulations contain acamprosate calcium - . . University of Alberta. 2017-11-19 [2017-11-26].
Acamprosate is thought to stabilize the chemical balance in the brain that would otherwise be disrupted by alcoholism, possibly by blocking glutaminergic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, while gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors are activated. ... The mechanism of action of acamprosate in the maintenance of alcohol abstinence is not completely understood. Chronic alcohol exposure is hypothesized to alter the normal balance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. in vitro and in vivo studies in animals have provided evidence to suggest acamprosate may interact with glutamate and GABA neurotransmitter systems centrally, and has led to the hypothesis that acamprosate restores this balance. It seems to inhibit NMDA receptors while activating GABA receptors.
- Kalk NJ, Lingford-Hughes AR. . British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. February 2014, 77 (2): 315–323. PMC 4014018
 . PMID 23278595. doi:10.1111/bcp.12070. 温哥华格式错误 (帮助)
. PMID 23278595. doi:10.1111/bcp.12070. 温哥华格式错误 (帮助) - Mason BJ, Heyser CJ. . CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets. March 2010, 9 (1): 23–32. PMC 2853976
 . PMID 20201812. doi:10.2174/187152710790966641.
. PMID 20201812. doi:10.2174/187152710790966641. - Azevedo, Andréia A.; Figueiredo, Ricardo R. . Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. Sep-Oct 2005, 71 (5) [2024-02-04].
- Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE. . Sydor A, Brown RY (编). 2nd. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2009: 372. ISBN 9780071481274.
- Möykkynen T, Korpi ER. . Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. July 2012, 111 (1): 4–13. PMID 22429661. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2012.00879.x
 .
. - Tsai G, Coyle JT. . Annual Review of Medicine. 1998, 49: 173–184. PMID 9509257. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.49.1.173.
- Tsai GE, Ragan P, Chang R, Chen S, Linnoila VM, Coyle JT. . The American Journal of Psychiatry. June 1998, 155 (6): 726–732. PMID 9619143.
- De Witte P, Littleton J, Parot P, Koob G. . CNS Drugs. 2005, 19 (6): 517–537. PMID 15963001. S2CID 11563216. doi:10.2165/00023210-200519060-00004.
- Mayer S, Harris BR, Gibson DA, Blanchard JA, Prendergast MA, Holley RC, Littleton J. . Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. October 2002, 26 (10): 1468–1478. PMID 12394279. doi:10.1097/00000374-200210000-00003.
- al Qatari M, Khan S, Harris B, Littleton J. . Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. September 2001, 25 (9): 1276–1283. PMID 11584146. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2001.tb02348.x.
- Trevor AJ. . Katzung BG (编). 14th. New York. 2017. ISBN 9781259641152. OCLC 1015240036.
- Berfield S. . Bloomberg Businessweek. 2002-05-27.
- Yahn, Stephanie L.; Watterson, Lucas R. . Substance Abuse:Research and Treatment. 2013-01-31, 7 (2013) [2023-4-02-04]. doi:10.4137/SART.S9345.
- . Forest Labs via Evaluate Group. 2001-10-23.
- . FDA Talk Paper. Food and Drug Administration. 2004-07-29 [2009-08-15]. (原始内容存档于2008-01-17).
- . DrugPatentWatch. [2017-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2017-12-01) (英语).
- . AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. [2017-11-27] (英语).
- Mann K, Kiefer F, Spanagel R, Littleton J. . Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. July 2008, 32 (7): 1105–1110. PMID 18540918. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00690.x.