UDP-Glucuronat-Decarboxylase
Die UDP-Glucuronat-Decarboxylase (UGD) ist das Enzym, das in Eukaryoten die Abspaltung von Kohlenstoffdioxid von UDP-Glucuronat katalysiert. Die dabei entstehende UDP-Xylose ist in Pflanzen für die Biosynthese der Xylose und weiterer Pentosen notwendig. Wirbeltiere benötigen UDP-Xylose allein zur Herstellung der Glycosaminoglycane (Knorpel). UGD ist in der Membran des Golgi-Apparats lokalisiert.[2][3]
| UDP-Glucuronat-Decarboxylase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 420 Aminosäuren | |
| Kofaktor | NAD | |
| Isoformen | 3 | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Namen | UXS1 SDR6E1; UGD | |
| Externe IDs | ||
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 4.1.1.35, Lyase | |
| Reaktionsart | Abspaltung von CO2 | |
| Substrat | UDP-Glucuronat | |
| Produkte | UDP-Xylose + CO2 | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Eukaryoten[1] | |
| Orthologe | ||
| Mensch | Hausmaus | |
| Entrez | 80146 | 67883 |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000115652 | ENSMUSG00000057363 |
| UniProt | Q8NBZ7 | Q91XL3 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001253875 | NM_026430 |
| Refseq (Protein) | NP_001240804 | NP_080706 |
| Genlocus | Chr 2: 106.09 – 106.19 Mb | Chr 1: 43.75 – 43.83 Mb |
| PubMed-Suche | 80146 | 67883 |
Katalysierte Reaktion
 ⇒
⇒ 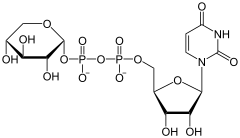 + CO2
+ CO2
UDP-α-D-Glucuronat wird zu UDP-α-D-Xylose umgesetzt.
Einzelnachweise
- Homologe bei OMA
- UniProt Q8NB27
- Moriarity JL, Hurt KJ, Resnick AC, et al.: UDP-glucuronate decarboxylase, a key enzyme in proteoglycan synthesis: cloning, characterization, and localization. In: J. Biol. Chem. 277. Jahrgang, Nr. 19, Mai 2002, S. 16968–75, doi:10.1074/jbc.M109316200, PMID 11877387 (jbc.org).
Weblinks
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Uronsäuren-Stoffwechsel – Lern- und Lehrmaterialien
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.