Polyoxine
Die Polyoxine sind eine Gruppe von Nukleosid-Antibiotika. Sie werden aus Streptomyces-Arten wie Streptomyces cacaoi gewonnen. Polyoxine sind wasserlöslich und werden im japanischen Reisanbau als Fungizide eingesetzt. Sie wirken durch Hemmung der Chitin-Biosynthese.[1]
| Name | CAS-Nummer | Summenformel | Molmasse [g·mol−1] | Schmelzpunkt [°C] | Siehe Formel | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyoxin A | 19396-03-3 | C23H32N6O14 | 616,54 | amorph | 1 | CH2OH | X | OH |
| Polyoxin B | 19396-06-6 | C17H25N5O13 | 507,41 | amorph | 1 | CH2OH | OH | OH |
| Polyoxin D | 22976-86-9 | C17H23N5O14 | 521,39 | >190
(zersetzt sich) |
1 | COOH | OH | OH |
| Polyoxin E | 22976-87-0 | C17H23N5O13 | 505,39 | >180
(zersetzt sich) |
1 | COOH | OH | H |
| Polyoxin F | 23116-76-9 | C23H30N6O15 | 630,52 | >190
(zersetzt sich) |
1 | COOH | X | OH |
| Polyoxin G | 22976-88-1 | C17H25N5O12 | 491,41 | >190
(zersetzt sich) |
1 | CH2OH | OH | H |
| Polyoxin H | 24695-54-3 | C23H32N6O13 | 600,54 | – | 1 | CH3 | X | OH |
| Polyoxin J | 22976-89-2 | C17H25N5O12 | 491,41 | amorph | 1 | CH3 | OH | OH |
| Polyoxin K | 22886-46-0 | C22H30N6O13 | 586,51 | amorph | 1 | H | X | OH |
| Polyoxin L | 22976-90-5 | C16H23N5O12 | 477,38 | amorph | 1 | H | OH | OH |
| Polyoxin M | 34718-88-2 | C16H23N5O11 | 461,39 | – | 1 | H | OH | H |
| Polyoxin C | 21027-33-8 | C11H15N3O8 | 317,26 | 260 – 267 | 2 | R = OH | ||
| Polyoxin I | 22886-33-5 | C17H22N4O9 | 426,38 | amorph | 2 | R = X | ||
| Polyoxin N | 37362-29-1 | C16H23N5O12 | 477,38 | 190
(zersetzt sich) |
3 | R = OH | ||
| Polyoxin O | 37362-28-0 | C16H23N5O11 | 461,39 | >190
(zersetzt sich) |
3 | R = H | ||
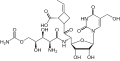 Polyoxin A
Polyoxin A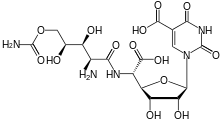 Polyoxin D
Polyoxin D

Strukturformel 1

Strukturformel 2

Substituent X

Strukturformel 3
Literatur
- Guoqing Niu, Huarong Tan: Nucleoside antibiotics: biosynthesis, regulation, and biotechnology. In: Trends in Microbiology. 2014, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2014.10.007.
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu Polyoxine. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 18. Januar 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.