Leucinol
Leucinol ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der chiralen 1,2-Aminoalkohole. Leucinol kann aus der Aminosäure Leucin gewonnen werden, weshalb es zumeist, wie auch Leucin, enantiomerenrein in der (S)-Konfiguration vorliegt. Das Enantiomer (R)-Leucinol und das racemische (RS)-Leucinol besitzen nur geringe Bedeutung.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
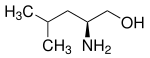 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (S)-Leucinol | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Leucinol | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C6H15NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
klare bis gelborange Flüssigkeit[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 117,19 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,917 g·cm−3[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
210 °C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Gewinnung und Darstellung
(S)-Leucinol kann durch Reduktion von (S)-Leucin mit Boran-Dimethylsulfid-Komplex hergestellt werden.[3]
Verwendung
(S)-Leucinol kann in der Synthese von enantiomerenreinen Oxazolin-Katalysatoren verwendet werden[4] und findet Anwendung als Katalysator in enantioselektiven Aldol-Reaktionen[5] sowie in chiralen stationären Phasen für die Chromatographie.[6][7]
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu L-Leucinol bei TCI Europe, abgerufen am 22. Dezember 2022.
- Datenblatt L-Leucinol bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 21. Dezember 2022 (PDF).
- D. A. Dickman, A. I. Meyers, G. A. Smith, R. E. Gawley: REDUCTION OF α-AMINO ACIDS: L-VALINOL In: Organic Syntheses. 63, 1985, S. 136, doi:10.15227/orgsyn.063.0136; Coll. Vol. 7, 1990, S. 530 (PDF).
- Helen A. McManus, Patrick J. Guiry: Recent Developments in the Application of Oxazoline-Containing Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis. In: Chemical Reviews. Band 104, Nr. 9, 2004, S. 4151–4202, doi:10.1021/cr040642v.
- Mikhail A. Kabeshov, Ondřej Kysilka, Lubomír Rulíšek, Yury V. Suleimanov, Marco Bella, Andrei V. Malkov, Pavel Kočovský: Cross-Aldol Reaction of Isatin with Acetone Catalyzed by Leucinol: A Mechanistic Investigation. In: Chemistry - A European Journal. Band 21, Nr. 34, 2015, S. 12026–12033, doi:10.1002/chem.201500536.
- Myung Ho Hyun, Jae-Jeong Ryoo: Optical Resolution of Racemic α-Amino Acids on a Dynamic Chiral Stationary Phase Derived from (S)-Leucinol by Ligand Exchange Chromatography. In: Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies. Band 19, Nr. 16, 1996, S. 2635–2648, doi:10.1080/10826079608014044.
- Jin Joo Ha, Hye Jee Han, Hee Eun Kim, Jong Sung Jin, Euh Duck Jeong, Myung Ho Hyun: Development of an improved ligand exchange chiral stationary phase based on leucinol for the resolution of proton pump inhibitors. In: Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. Band 100, 2014, S. 88–93, doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.029.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
