Fluortelomersulfonsäuren
Fluortelomersulfonsäuren (FTSA, teilweise auch FTS) sind eine zu den Fluortelomeren und damit zu den per- und polyfluorierten Alkylverbindungen (PFAS) gehörende Stoffgruppe. Die allgemeine Summenformel lautet CF3(CF2)nCH2CH2SO3H, wobei n nur ungerade sein kann.[1]
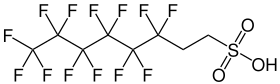
6:2-Fluortelomersulfonsäure (6:2-FTSA)
FTSA werden mittels Telomerisation hergestellt.[2]
Derivate von FTSA wie 6:2-FTAB werden in Schaumlöschmitteln (AFFF) eingesetzt.[3][4]
In der Umwelt und in Organismen können FTSA in Perfluorcarbonsäuren (PFCA) umgewandelt werden.[5][6][7]
Systematik
| Per- und polyfluorierte Alkylverbindungen (PFAS)[8] | |||||||||||||
| Nicht-Polymere | |||||||||||||
| Perfluorierte Alkylverbindungen | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkylsäuren (PFAA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluorcarbonsäuren (PFCA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluorsulfonsäuren (PFSA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluorphosphonsäuren (PFPA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkylethersäuren (PFEA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkylethercarbonsäuren (PFECA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkylethersulfonsäuren (PFESA) | |||||||||||||
| Polyfluorierte Alkylverbindungen | |||||||||||||
| Fluortelomere | |||||||||||||
| Fluortelomercarbonsäuren (FTCA) | |||||||||||||
| Fluortelomersulfonsäuren (FTSA) | |||||||||||||
| Fluortelomeralkohole (FTOH) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkansulfonamidoverbindungen | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkansulfonamide (FASA) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkansulfonamidoethanole (FASE) | |||||||||||||
| Perfluoralkansulfonamidoessigsäuren (FASAA) | |||||||||||||
| Polymere | |||||||||||||
| Fluorpolymere | |||||||||||||
| Perfluorpolyether (PFPE) | |||||||||||||
| Seitenketten-fluorierte Polymere | |||||||||||||
Literatur
Einzelnachweise
- miljodirektoratet.no
- Hans-Joachim Lehmler: Synthesis of environmentally relevant fluorinated surfactants--a review. In: Chemosphere. Band 58, Nr. 11, März 2005, S. 1471–1496, doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.078, PMID 15694468.
- Huanting Zhao, Liping Yang, Xiaojing Yang, Shuyan Zhao: Behaviors of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonamide alkylbetaine (6:2 FTAB) in wheat seedlings: Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and ecotoxicity. In: Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. Band 238, 15. Juni 2022, S. 113585, doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113585.
- Lisa A. D’Agostino, Scott A. Mabury: Certain Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Associated with Aqueous Film Forming Foam Are Widespread in Canadian Surface Waters. In: Environmental Science & Technology. Band 51, Nr. 23, 5. Dezember 2017, S. 13603–13613, doi:10.1021/acs.est.7b03994, PMID 29110476.
- Wenping Zhang, Shimei Pang, Ziqiu Lin, Sandhya Mishra, Pankaj Bhatt, Shaohua Chen: Biotransformation of perfluoroalkyl acid precursors from various environmental systems: advances and perspectives. In: Environmental Pollution. Band 272, 1. März 2021, S. 115908, doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115908.
- Ashenafi Berhanu, Ishmael Mutanda, Ji Taolin, Majjid A. Qaria, Bin Yang, Daochen Zhu: A review of microbial degradation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Biotransformation routes and enzymes. In: Science of The Total Environment. Band 859, 10. Februar 2023, S. 160010, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160010.
- Zhiming Zhang, Dibyendu Sarkar, Jayanta Kumar Biswas, Rupali Datta: Biodegradation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A review. In: Bioresource Technology. Band 344, 1. Januar 2022, S. 126223, doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126223.
- EPA (Hrsg.): Multi-Industry Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Study. 2021 Preliminary Report. Washington DC September 2021, S. 29 (englisch, 81 S., epa.gov [PDF; 1,1 MB; abgerufen am 1. Februar 2023]).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.