Diacetylmonoxim
Diacetylmonoxim ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Oxime. Sie wirkt als Carboxylase- und Cholinesterase-Reaktivator und wird deshalb zur Behandlung von Organophosphatvergiftungen eingesetzt.[2]
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
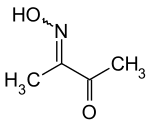 | ||||||||||||||||
| Vereinfachte Strukturformel – Gemisch von (E)- und (Z)-Isomer | ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | Diacetylmonoxim | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C4H7NO2 | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 101,10 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
185–186 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||||||||
Es ist außerdem Zwischenprodukt bei der Synthese von Diacetyldioxim.[3]
-biacetyl_dioxime_200.svg.png.webp) Diacetyldioxim
Diacetyldioxim
Einzelnachweise
- Datenblatt 2,3-Butanedione monoxime, ≥98% bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 29. Oktober 2013 (PDF).
- Raymond M. Dawson: The diacetylmonoxime assay of urea, its application to the assay of diacetylmonoxime and a comparison with other methods for the analysis of diacetylmonoxime. In: Journal of Applied Toxicology. Band 13, Nr. 4, 1993, S. 277–282, doi:10.1002/jat.2550130410.
- K. H. Slotta, K. R. Jacobi: Herstellung organischer Reagenzien im analytischen Laboratorium. III. Diacetyldioxim. In: Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie. Band 83, Nr. 1-2, Januar 1931, S. 1–5, doi:10.1007/bf01361818.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.