Allyloxycarbonyl-Gruppe
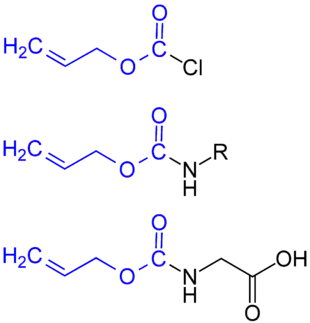
Die Allyloxycarbonyl-Gruppe, in Fachkreisen üblicherweise mit Alloc abgekürzt, ähnelt der Benzyloxycarbonyl-Gruppe (Cbz-Gruppe) und findet als Schutzgruppe in der chemischen Synthese von Peptiden Verwendung.
Benutzt wird die Alloc-Schutzgruppe für den Schutz von α-Aminogruppen, jedoch auch für den Schutz von Seitengruppen, besonders bei der Synthese cyclischer Peptide. Die Alloc-Schutzgruppe ist unter basischen und sauren Bedingungen stabil und kann durch Einwirkung von Tetrakis(triphenylphosphan)palladium(0) und einem geeigneten Nucleophil abgespalten werden.[1]
Die Alloc-Gruppe wird meist als Chlorkohlensäureester (AllocCl) zum Schützen von Aminogruppen eingesetzt.[2]
Einzelnachweise
- Sherine N. Khattab, Ramon Subirós-Funosas, Ayman El-Faham, Fernando Albericio: Oxime Carbonates: Novel Reagents for the Introduction of Fmoc and Alloc Protecting Groups, Free of Side Reactions, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 3275–3280.
- P. Gómez-Martinez, M. Dessolin, F. Guibé, F. Albericio, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1999, 2871–2874.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.