লোদি রাজবংশ
লোদি রাজবংশ ছিল পশতু রাজবংশ।[4] ১৪৫১ থেকে ১৫২৬ সাল পর্যন্ত উত্তর ভারত ও পাঞ্জাবের অংশবিশেষ ও বর্তমান পাকিস্তানের খাইবার পাখতুনখোয়া প্রদেশে লোদি রাজবংশের শাসন ছিল। বাহলুল খান লোদি এই রাজবংশের সূচনা করেন।[5]
লোদি রাজবংশ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ১৪৫১–১৫২৬ | |||||||||
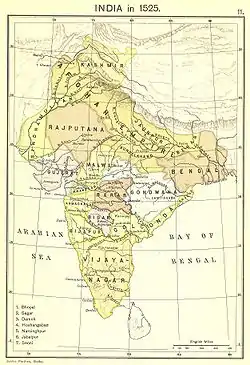 লোদি রাজবংশের অধীনে অঞ্চলটি দেখানো মানচিত্র, আফগান সাম্রাজ্য হিসাবে চিহ্নিত[2] | |||||||||
| রাজধানী | দিল্লি | ||||||||
| প্রচলিত ভাষা | ফারসি[3] | ||||||||
| ধর্ম | সুন্নি ইসলাম | ||||||||
| সরকার | রাজতন্ত্র | ||||||||
| ইতিহাস | |||||||||
• প্রতিষ্ঠা | ১৪৫১ | ||||||||
• বিলুপ্ত | ১৫২৬ | ||||||||
| |||||||||
ইবরাহিম লোদির আমলে লোদি রাজবংশের পতন ঘটে। তিনি মেবারের রানা সাঙ্গার সাথে কাছ থেকে বেশ কিছু আক্রমণের সম্মুখীন হন। রানা সাঙ্গা লোদিদেরকে বেশ কয়েকবার পরাজিত করে ফলে রাজ্য দুর্বল হয়ে পড়ে। ইবরাহিম লোদি বাবরের কাছে পরাজিত হওয়ার পর লোদি রাজবংশের সমাপ্তি ঘটে। বাবর মুঘল রাজবংশের সূচনা করেন।
আরও দেখুন
- লোদি (পশতু গোত্র)
- লোদি উদ্যান
- সুন্নি মুসলিম রাজবংশের তালিকা
তথ্যসূত্র
- Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (১৯৭৮)। A Historical atlas of South Asia। Chicago: University of Chicago Press। পৃষ্ঠা 147, map XIV.4 (d)। আইএসবিএন 0226742210।
- Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (১৯৭৮)। A Historical atlas of South Asia। Chicago: University of Chicago Press। পৃষ্ঠা 147, map XIV.4 (d)। আইএসবিএন 0226742210।
- "Arabic and Persian Epigraphical Studies - Archaeological Survey of India"। Asi.nic.in। ২০১১-০৯-২৯ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০১০-১১-১৪।
- "Lodī dynasty"। Encyclopedia Britannica (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০১৮-১০-১০।
- Sen, Sailendra (২০১৩)। A Textbook of Medieval Indian History। Primus Books। পৃষ্ঠা 122–125। আইএসবিএন 978-9-38060-734-4।
আরো পড়ুন
- Desoulières, Alain (১৯৮৮)। "Mughal Diplomacy in Gujarat (1533-1534) in Correia's 'Lendas da India'"। Modern Asian Studies। 22 (3): 433–454। আইএসএসএন 0026-749X।
- Haider, Najaf (১৯৯৬)। "Precious Metal Flows and Currency Circulation in the Mughal Empire"। Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient। 39 (3): 298–364। আইএসএসএন 0022-4995।
- India. Indian History: Medieval History. 2005.
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Chandigarh Stories"। www.tribuneindia.com। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২০২১-০৯-১২।
- Richards, John F. (১৯৬৫)। "The Economic History of the Lodi Period: 1451-1526"। Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient। 8 (1): 47–67। আইএসএসএন 0022-4995। ডিওআই:10.2307/3596342।
- SarDesai, D.R. India The Definitive History. Colorado: Westview Press, 2008.
- Subrahmanyam, Sanjay (২০০০)। "A Note on the Rise of Surat in the Sixteenth Century"। Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient। 43 (1): 23–33। আইএসএসএন 0022-4995।
- The World Book Encyclopedia, 1979 ed. “Mogul Empire.”
- ud-Din, Hameed (১৯৬২)। "Historians of Afghan Rule in India"। Journal of the American Oriental Society। 82 (1): 44–51। আইএসএসএন 0003-0279। ডিওআই:10.2307/595978।
- Desoulieres, Alain (১৯৮৮)। "Mughal Diplomacy in Gujarat (1533–1534) in Correia's 'Lendas da India'"। Modern Asian Studies। 22 (3): 454। জেস্টোর 312590। ডিওআই:10.1017/s0026749x00009616।
- Haider, Najaf (১৯৯৬)। "Precious Metal Flows and Currency Circulation in the Mughal Empire"। Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient। 39 (3): 298–364। জেস্টোর 3632649। ডিওআই:10.1163/1568520962601180।
- Sharma, Gopinath (১৯৫৪)। Mewar & the Mughal Emperors (1526-1707 A.D.) (ইংরেজি ভাষায়)। S.L. Agarwala।
- Subrahmanyam, Sanjay (২০০০)। "A Note on the Rise of Surat in the Sixteenth Century"। Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient। 43 (1): 23–33। জেস্টোর 3632771। ডিওআই:10.1163/156852000511222।
- Ud-Din, Hameed (জানুয়ারি–মার্চ ১৯৬২)। "Historians of Afghan Rule in India"। Journal of the American Oriental Society। 82 (1): 44–51। জেস্টোর 595978। ডিওআই:10.2307/595978।
বহিঃসংযোগ
উইকিমিডিয়া কমন্সে লোদি রাজবংশ সংক্রান্ত মিডিয়া রয়েছে।
- A History of Sind, Volume II, Translated from Persian Books by Mirza Kalichbeg Fredunbeg, chpt. 68
- The Sayyids and the Lodhis
- WebIndia - History (Deli Sultanate)
টেমপ্লেট:Pashtun
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.