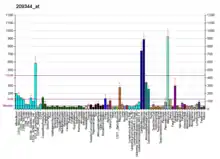
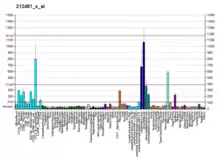
TPM4
TPM4 (Tropomyosin 4) هوَ بروتين يُشَفر بواسطة جين TPM4 في الإنسان.[1][2]
الوظيفة
المراجع
- Wilton SD، Lim L، Dorosz SD، Gunn HC، Eyre HJ، Callen DF، Laing NG (يوليو 1996). "Assignment of the human alpha-tropomyosin gene TPM4 to band 19p13.1 by fluorescence in situ hybridization". Cytogenet Cell Genet. ج. 72 ع. 4: 294–6. DOI:10.1159/000134206. PMID:8641132.
- "Entrez Gene: TPM4 tropomyosin 4". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2010-12-05.
قراءة متعمقة
- Rasmussen HH، van Damme J، Puype M، وآخرون (1993). "Microsequences of 145 proteins recorded in the two-dimensional gel protein database of normal human epidermal keratinocytes". Electrophoresis. ج. 13 ع. 12: 960–9. DOI:10.1002/elps.11501301199. PMID:1286667.
- MacLeod AR، Talbot K، Smillie LB، Houlker C (1987). "Characterization of a cDNA defining a gene family encoding TM30p1, a human fibroblast tropomyosin". J. Mol. Biol. ج. 194 ع. 1: 1–10. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(87)90710-8. PMID:3612796.
- MacLeod AR، Houlker C، Reinach FC، وآخرون (1986). "A muscle-type tropomyosin in human fibroblasts: evidence for expression by an alternative RNA splicing mechanism". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 82 ع. 23: 7835–9. DOI:10.1073/pnas.82.23.7835. PMC:390864. PMID:3865200.
- Lawrence B، Perez-Atayde A، Hibbard MK، وآخرون (2000). "TPM3-ALK and TPM4-ALK oncogenes in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors". Am. J. Pathol. ج. 157 ع. 2: 377–84. DOI:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64550-6. PMC:1850130. PMID:10934142.
- Meech SJ، McGavran L، Odom LF، وآخرون (2001). "Unusual childhood extramedullary hematologic malignancy with natural killer cell properties that contains tropomyosin 4--anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene fusion". Blood. ج. 98 ع. 4: 1209–16. DOI:10.1182/blood.V98.4.1209. PMID:11493472.
- Yi J، Kloeker S، Jensen CC، وآخرون (2002). "Members of the Zyxin family of LIM proteins interact with members of the p130Cas family of signal transducers". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 277 ع. 11: 9580–9. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M106922200. PMID:11782456.
- Strausberg RL، Feingold EA، Grouse LH، وآخرون (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 99 ع. 26: 16899–903. DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC:139241. PMID:12477932.
- Gevaert K، Goethals M، Martens L، وآخرون (2004). "Exploring proteomes and analyzing protein processing by mass spectrometric identification of sorted N-terminal peptides". Nat. Biotechnol. ج. 21 ع. 5: 566–9. DOI:10.1038/nbt810. PMID:12665801.
- Ota T، Suzuki Y، Nishikawa T، وآخرون (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. ج. 36 ع. 1: 40–5. DOI:10.1038/ng1285. PMID:14702039.
- Lin KT، Lu RM، Tarn WY (2004). "The WW domain-containing proteins interact with the early spliceosome and participate in pre-mRNA splicing in vivo". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 24 ع. 20: 9176–85. DOI:10.1128/MCB.24.20.9176-9185.2004. PMC:517884. PMID:15456888.
- Gerhard DS، Wagner L، Feingold EA، وآخرون (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. ج. 14 ع. 10B: 2121–7. DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC:528928. PMID:15489334.
- Bruneel A، Labas V، Mailloux A، وآخرون (2006). "Proteomics of human umbilical vein endothelial cells applied to etoposide-induced apoptosis". Proteomics. ج. 5 ع. 15: 3876–84. DOI:10.1002/pmic.200401239. PMID:16130169.
- Rual JF، Venkatesan K، Hao T، وآخرون (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. ج. 437 ع. 7062: 1173–8. DOI:10.1038/nature04209. PMID:16189514.
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
- بوابة الكيمياء الحيوية
- بوابة طب
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.