NOL5A
NOL5A (NOP56 ribonucleoprotein) هوَ بروتين يُشَفر بواسطة جين NOL5A في الإنسان.[1][2]
| NOP56 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| المعرفات | |||||||||||||||||
| الأسماء المستعارة | NOP56, NOL5A, SCA36, ribonucleoprotein | ||||||||||||||||
| معرفات خارجية | الوراثة المندلية البشرية عبر الإنترنت 614154 MGI: MGI:1914384 HomoloGene: 4660 GeneCards: 10528 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| نمط التعبير عن الحمض النووي الريبوزي | |||||||||||||||||
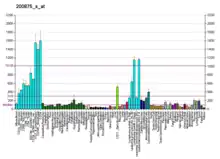 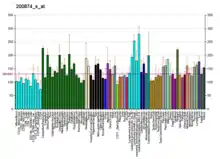 | |||||||||||||||||
| المزيد من بيانات التعبير المرجعية | |||||||||||||||||
| أورثولوج | |||||||||||||||||
| الأنواع | الإنسان | الفأر | |||||||||||||||
| أنتريه | 10528 | 67134 | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000101361 | ENSMUSG00000027405 | |||||||||||||||
| يونيبروت | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (مرسال ر.ن.ا.) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (بروتين) | |||||||||||||||||
| الموقع (UCSC | n/a | Chr 2: 130.12 – 130.12 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| بحث ببمد | |||||||||||||||||
| ويكي بيانات | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
الوظيفة
المراجع
- "Entrez Gene: NOL5A nucleolar protein 5A (56kDa with KKE/D repeat)". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2010-12-05.
- Gautier T، Berges T، Tollervey D، Hurt E (ديسمبر 1997). "Nucleolar KKE/D repeat proteins Nop56p and Nop58p interact with Nop1p and are required for ribosome biogenesis". Mol Cell Biol. ج. 17 ع. 12: 7088–98. PMC:232565. PMID:9372940.
قراءة متعمقة
- Deloukas P؛ Matthews LH؛ Ashurst J؛ وآخرون (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. ج. 414 ع. 6866: 865–71. DOI:10.1038/414865a. PMID:11780052.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Andersen JS؛ Lyon CE؛ Fox AH؛ وآخرون (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. ج. 12 ع. 1: 1–11. DOI:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID:11790298.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Watkins NJ، Dickmanns A، Lührmann R (2003). "Conserved stem II of the box C/D motif is essential for nucleolar localization and is required, along with the 15.5K protein, for the hierarchical assembly of the box C/D snoRNP". Mol. Cell. Biol. ج. 22 ع. 23: 8342–52. DOI:10.1128/MCB.22.23.8342-8352.2002. PMC:134055. PMID:12417735.
- Scherl A؛ Couté Y؛ Déon C؛ وآخرون (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus". Mol. Biol. Cell. ج. 13 ع. 11: 4100–9. DOI:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC:133617. PMID:12429849.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Strausberg RL؛ Feingold EA؛ Grouse LH؛ وآخرون (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 99 ع. 26: 16899–903. DOI:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC:139241. PMID:12477932.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Hayano T؛ Yanagida M؛ Yamauchi Y؛ وآخرون (2003). "Proteomic analysis of human Nop56p-associated pre-ribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes. Possible link between Nop56p and the nucleolar protein treacle responsible for Treacher Collins syndrome". J. Biol. Chem. ج. 278 ع. 36: 34309–19. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M304304200. PMID:12777385.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Ota T؛ Suzuki Y؛ Nishikawa T؛ وآخرون (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. ج. 36 ع. 1: 40–5. DOI:10.1038/ng1285. PMID:14702039.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Hassel S؛ Eichner A؛ Yakymovych M؛ وآخرون (2004). "Proteins associated with type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMPR-II) and identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry". Proteomics. ج. 4 ع. 5: 1346–58. DOI:10.1002/pmic.200300770. PMID:15188402.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Gerhard DS؛ Wagner L؛ Feingold EA؛ وآخرون (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. ج. 14 ع. 10B: 2121–7. DOI:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC:528928. PMID:15489334.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Watkins NJ؛ Lemm I؛ Ingelfinger D؛ وآخرون (2005). "Assembly and maturation of the U3 snoRNP in the nucleoplasm in a large dynamic multiprotein complex". Mol. Cell. ج. 16 ع. 5: 789–98. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.012. PMID:15574333.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Andersen JS؛ Lam YW؛ Leung AK؛ وآخرون (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. ج. 433 ع. 7021: 77–83. DOI:10.1038/nature03207. PMID:15635413.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Nousiainen M؛ Silljé HH؛ Sauer G؛ وآخرون (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. ج. 103 ع. 14: 5391–6. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC:1459365. PMID:16565220.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - Olsen JV؛ Blagoev B؛ Gnad F؛ وآخرون (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. ج. 127 ع. 3: 635–48. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID:17081983.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|name-list-format=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة)
- بوابة طب
- بوابة الكيمياء الحيوية
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.