كيمياء ضيف-مضيف
كيمياء ضيف-مضيف هي جزء من كيمياء الجزيئات الضخمة،[3] توصف فيه المعقدات التي يحتوي فيها جزيء ضخم (المضيف) جزيئاً أو أيوناً أصغر (ضيف) في تجويفه، مع وجود تآثرات غير تساهمية، والتي تجعل الكيان متماسكاً.
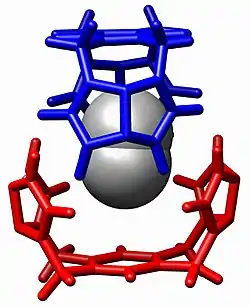
البنية البلورية لمعقد ضيف-مضيف يحل فيها مركب بارا-زيليلين ثنائي الأمونيوم داخل كوكوربيتوريل.[1]
تشمل التآثرات غير تساهمية كل من الرابطة الأيونية والرابطة الهيدروجينية وقوى فان دير فالس والتآثرات الهيدروفوبية (الدافعة للماء).[4]
مراجع
- Freeman، Wade A. (1984). "Structures of the p-xylylenediammonium chloride and calcium hydrogensulfate adducts of the cavitand 'cucurbituril', C36H36N24O12". Acta Crystallographica B. ج. 40: 382–387. DOI:10.1107/S0108768184002354.
- Valdés، Carlos؛ Toledo، Leticia M.؛ Spitz، Urs؛ Rebek، Julius (1996). "Structure and Selectivity of a Small Dimeric Encapsulating Assembly". Chem. Eur. J. ج. 2: 989–991. DOI:10.1002/chem.19960020814.
- Steed، Jonathan W.؛ Atwood، Jerry L. (2009). Supramolecular Chemistry (ط. 2nd.). Wiley. ص. 1002. ISBN:978-0-470-51234-0.
- Lodish, H.؛ Berk, A.؛ Kaiser, C. (2008). Molecular Cell Biology. ISBN:978-0-7167-7601-7.
- بوابة الفيزياء
- بوابة الكيمياء
- بوابة كيمياء فيزيائية
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.