تكامل لوبيغ
في الرياضيات، يُعدّ التكامل لدالة غير سلبية لمتغير واحد في أبسط الحالات كالمساحة بين الرسم البياني لتلك الدالة والمحور x.[1][2] يمتد تكامل لوبيغ إلى الدوال من الدرجات الأعلى. كما أنه يوسع المجالات التي يمكن تعريف هذه الدوال عليها.

يمكن تفسير تكامل دالة إيجابية كمساحة تحت منحنى.
تفسير بديهي

تكامل ريمان داربوكس (باللون الأزرق) وتكامل لوبيغ (باللون الأحمر).
لفهم الأساليب المختلفة للتكامل، دعنا نتخيل أننا نريد أن نجد حجم جبل (فوق مستوى سطح البحر).
- نهج ريمان داربوكس
- باستخدام هذه الطريقة للتكامل نقوم بتقسيم قاعدة الجبل إلى شبكة من المربعات مساحتها متر واحد. ثم نقوم بقياس ارتفاع الجبل في وسط كل مربع. الحجم مقسوماً على مربع شبكة واحد يساوي تقريباً 1متر مربع × (ارتفاع ذلك المربع)، لذا فإن الحجم الإجمالي هو 1م 2 مضروباً في مجموع الارتفاعات.
- نهج لوبيغ
- ارسم خريطة خطوط منسوبة للجبل بحيث يبلغ ارتفاع الخطوط المجاورة 1 متر لكل منها. يبلغ حجم الأرض التي يحتويها شكل الخط المنسوب واحد حوالي 1م × (مساحة الشكل)، لذا فإن الحجم الإجمالي هو مجموع هذه المناطق مضروبة في 1م.
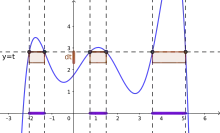
في الصورة دالة قابلة للقياس مع المجموعة (على المحور السيني). يتم الحصول على تكامل لوبيغ عن طريق تقطيع شرائح على امتداد المحور ص، باستخدام مقياس لوبيغ أحادي البعد لقياس "عرض" الشرائح.
ملاحظات
- "معلومات عن تكامل لوبيغ على موقع babelnet.org". babelnet.org. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2020-10-28.
- "معلومات عن تكامل لوبيغ على موقع id.ndl.go.jp". id.ndl.go.jp. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-03-05.
المراجع
- Bartle، Robert G. (1995). The elements of integration and Lebesgue measure. Wiley Classics Library. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. xii+179. ISBN:0-471-04222-6. MR:1312157.
- Bauer، Heinz (2001). Measure and Integration Theory. De Gruyter Studies in Mathematics 26. Berlin: De Gruyter. 236. ISBN:978-3-11-016719-1.
- Bourbaki، Nicolas (2004). Integration. I. Chapters 1–6. Translated from the 1959, 1965 and 1967 French originals by Sterling K. Berberian. Elements of Mathematics (Berlin). Berlin: Springer-Verlag. xvi+472. ISBN:3-540-41129-1. MR:2018901.
- Dudley، Richard M. (1989). Real analysis and probability. The Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Mathematics Series. Pacific Grove, CA: Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software. xii+436. ISBN:0-534-10050-3. MR:0982264. Very thorough treatment, particularly for probabilists with good notes and historical references.
- Folland، Gerald B. (1999). Real analysis: Modern techniques and their applications. Pure and Applied Mathematics (New York) (ط. Second). New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. xvi+386. ISBN:0-471-31716-0. MR:1681462.
- Halmos، Paul R. (1950). Measure Theory. New York, N. Y.: D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc. ص. xi+304. MR:0033869. A classic, though somewhat dated presentation.
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Lebesgue integral", Encyclopedia of Mathematics (بالإنجليزية), Springer, ISBN:978-1-55608-010-4
- Lebesgue، Henri (1904). "Leçons sur l'intégration et la recherche des fonctions primitives". Gauthier-Villars. Paris.
- Lebesgue, Henri (1972). Oeuvres scientifiques (en cinq volumes) (بالفرنسية). Geneva: Institut de Mathématiques de l'Université de Genève. p. 405. MR:0389523.
- Lieb، Elliott؛ Loss، Michael (2001). Analysis. Graduate Studies in Mathematics (ط. 2nd). جمعية الرياضيات الأمريكية. ج. 14. ISBN:978-0821827833.
- Loomis، Lynn H. (1953). An introduction to abstract harmonic analysis. Toronto-New York-London: D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc. ص. x+190. MR:0054173. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2022-04-07. Includes a presentation of the Daniell integral.
- Munroe، M. E. (1953). Introduction to measure and integration. Cambridge, Mass.: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc. ص. x+310. MR:0053186. Good treatment of the theory of outer measures.
- Royden، H. L. (1988). Real analysis (ط. Third). New York: Macmillan Publishing Company. ص. xx+444. ISBN:0-02-404151-3. MR:1013117.
- Rudin، Walter (1976). Principles of mathematical analysis. International Series in Pure and Applied Mathematics (ط. Third). New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. ص. x+342. MR:0385023. Known as Little Rudin, contains the basics of the Lebesgue theory, but does not treat material such as Fubini's theorem.
- Rudin، Walter (1966). Real and complex analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co. ص. xi+412. MR:0210528. Known as Big Rudin. A complete and careful presentation of the theory. Good presentation of the Riesz extension theorems. However, there is a minor flaw (in the first edition) in the proof of one of the extension theorems, the discovery of which constitutes exercise 21 of Chapter 2.
- Saks، Stanisław (1937). Theory of the Integral. Monografie Matematyczne (ط. 2nd). وارسو-لفيف: G.E. Stechert & Co. ج. 7. JFM:63.0183.05. Zbl:0017.30004. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2021-05-06.
{{استشهاد بكتاب}}: روابط خارجية في|سلسلة= - Shilov، G. E.؛ Gurevich، B. L. (1977). Integral, measure and derivative: a unified approach. Translated from the Russian and edited by Richard A. Silverman. Dover Books on Advanced Mathematics. New York: Dover Publications Inc. xiv+233. ISBN:0-486-63519-8. MR:0466463. Emphasizes the Daniell integral.
- Siegmund-Schultze، Reinhard (2008)، "Henri Lebesgue"، في Timothy Gowers؛ June Barrow-Green؛ Imre Leader (المحررون)، Princeton Companion to Mathematics، Princeton University Press.
- Teschl، Gerald. Topics in Real and Functional Analysis. (lecture notes). مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-11-05.
- Yeh، James (2006). Real Analysis: Theory of Measure and Integral 2nd. Edition Paperback. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company Pte. Ltd. ص. 760. ISBN:978-981-256-6.
- بوابة تحليل رياضي
- بوابة رياضيات
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.