تفاعل جوليا
تفاعل جوليا (بالإنجليزية: Julia olefination) هو تفاعل فيالكيمياء العضوية يكونألكين. يتفاعل سلفون الفينيل (1) مع الدهيد (أو كيتون)، ليعطي المركب الوسيط (2) والذي بدوره يتحول للألكين (3) بعد إضافة الكحول والحذف الاختزالي باستخدام ملغمة الصوديوم آو ايوديد السماريوم الثنائي.
| تفاعل جوليا | |
|---|---|
مكتشف التفاعل هو العالم الفرنسي مارك جوليا
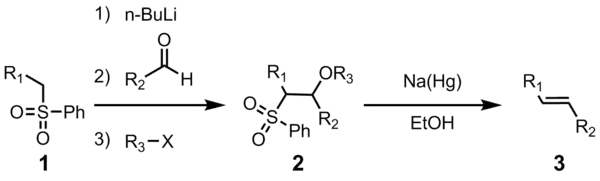
كل الخطوات السابقة يتم عملها في وعاء واحد كما أن استخدام الهاليد الثلاثي اختياري. تصفية الوسيط (2) يرع نقاوة المركب الناتج ويزيد من المحصول.
ميكيانيكية التفاعل
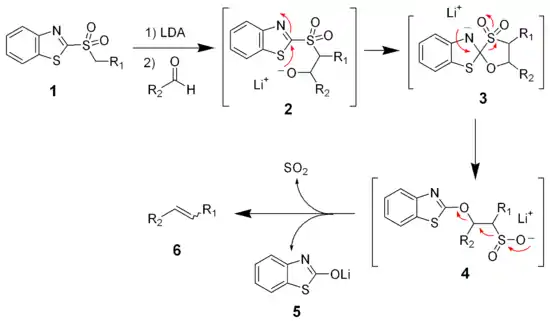
في الخطوة الأولي تنتزع القاعدة القوية بروتون من الكربوم المجاور للكبريت في السلفون (1)، الأنيون الناتج يتفاعل مع الألدهيد ليكون الألكوكسيل (3). الأكسوكسيل يتفاعل مع الهاليد الثلاثي لينتج المادة الوسيطة (4). ميكانيكية اختزال ملغمة الصوديوم غير معروفة تماماً، لكن تم إثبات أنها تمر عبر جذر حر (5). يتفاعل هذا الجذر مع المذيب ليلتقط ذرة هيدروجين ويكون المركب النهائي (6).
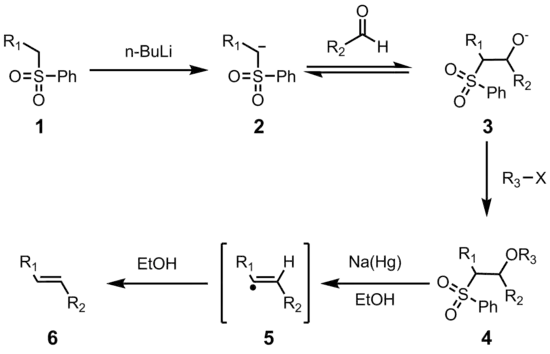
الكيمياء الفراغية للألكين الناتج لا تعتمد على السلفون الابتدائي لأن الترتيب الفراغي يختفي عند تكون الجذر الحر. الجذر الحر يك،ن في حالة اتزان بين سيس وترانس وفي العادة يفضل ترانس حيث أنه أقل طاقة من الناحية الثيرموديناميكية.
التطبيقات الصناعية
تفاعلات جوليا فعالة من حيث يسهل التحكم بها لتكوين مركبات طبيعية معقدة بتراكيب فراغية محددة.
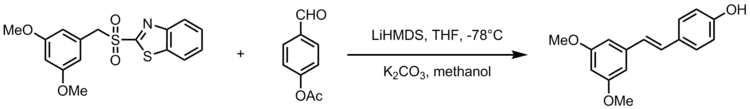
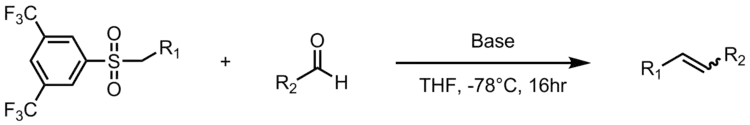
المصادر
- ^ Julia, M.; Paris, J.-M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 4833–4836. (دُوِي:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)87348-2)
- ^ Kocienski, P. J.; Lythgoe, B.; Ruston, S. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1978, 829.
- ^ Keck, G. E.; Savin, K. A.; Weglarz, M. A. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 3194–3204. (دُوِي:10.1021/jo00115a041)
- ^ Kocienski, P. J. Phosphorus and Sulfur 1985, 24, 97–127. (Review)
- ^ Kelly, S. E. Comp. Org. Syn. 1991, 1, 792–806. (Review)
- ^ Blakemore, P. R. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 2002, 2563–2585. ()
- ^ Baudin, J. B.; Hareau, G.; Julia, S. A.; Ruel, O. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 1175. (دُوِي:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)92037-9)
- ^ Truce, W. E.; Kreider, E. M.; Brand, W. W. Org. React. 1970, 18, 99. (Review)
- ^ Paul R. Blakemore, William J. Cole, Philip J. Kocieński, Andrew Morley Synlett 1998, 26–28. (دُوِي:10.1055/s-1998-1570)
- ^ Christophe Aïssa J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 360–63. (دُوِي:10.1021/jo051693a)
- ^ Zajc, B., & Kumar, R. (2010). Synthesis of Fluoroolefins via Julia-Kocienski Olefination. Synthesis, 2010(11), 1822–1836.(دُوِي:10.1055/s-0029-1218789)
- ^ Langcake, P.; Pryce, R. J. (1977). "A new class of phytoalexins from grapevines". Experientia 33 (2): 151–2. (دُوِي:10.1007/BF02124034) ببمد: 844529.
- ^ Moro, A. V.; Cardoso, F. S. P.; Correia, C. R. D. Heck arylation of styrenes with arenediazonium salts: Short, efficient, and stereoselective synthesis of resveratrol, DMU-212, and analogues. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49(39), 5668–5671.
- ^ Prabhakar Peddikotla, Amar G. Chittiboyina, Ikhlas A. Khan, (2014) ChemInform Abstract: Synthesis of Pterostilbene by Julia Olefination.. ChemInform 45:10.1002/chin.v45.8
- ^ Alonso DA, Fuensanta M, Nájera C, Varea M. J. Org. Chem. 2005; 70:6404–6416. [PubMed: 16050703]
- ^ A. B. Smith, III and B. M. Brandt. Total Synthesis of (–)-Callystatin A. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1685-1688.
- ^ Robiette, R.; Pospíšil, J. On the Origin of E/Z Selectivity in the Modified Julia Olefination: Importance of the Elimination Step; Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 836-840.
- بوابة الكيمياء